Water is a compound, made of H2O molecules. Without water, there is no existence of life on the planet. It is a most essential element. We use water in many different ways in our daily lives like drinking, washing, and other household needs, and on a large scale in industries. We use water in critical ways so there is a need to ensure the quality of water. Measuring the water quality is really important. You can test water quality in many chemical and physical parameters. Physical parameters include color, odor, etc. Chemical parameters include electrical conductivity, pH, total solids, the hardness of water, and total dissolved solids.
The main difference between TDS and hardness is that TDS hard water consists of organic and inorganic substances that cannot be filtered out through any filter paper. The hardness of the water exists due to the presence of magnesium and calcium salts of carbonate, chloride, and sulfate. Total Dissolved solids or TDS pertain to inorganic salts and some amount of organic compounds can dissolve in water. Water hardness refers to water that has a high amount of mineral content.
Table of Contents
Total Dissolved Solid (TDS)
DS (Dissolved Salts) in TDS (Total Dissolved Salts) mentions any mineral, metals, salts, anions, and cations that are mixed or dissolved in water. Now here is necessary to define TDS. The T in TDS refers to Dissolved Salts along with the traced amount of organic materials that are dissolved in water. We consider TDS when we want to analyze the quality of water of rivers, streams, and lakes as well as drinking water. TDS is a chemical parameter to test the quality of water.
Through TDS, we find out anything that is present in water except H2O. These small particles of dissolved solids cannot filter through a filter paper that has 2-micrometer pores. The soft water TDS level was measured in ppm (parts per million). Generally, explaining the TDS, cations, and anions are dissolved in water.
Measuring TDS:
Most people search for how to measure TDS. There are two ways through which you can do this.
- Gravimetric Method
- Electrical Conductivity Method
In the gravimetric method, the liquid evaporates. It is a traditional method and time time-consuming process. The residue that is left behind after evaporating the liquid is TDS and it is weighed to measure the quantity of TDS. Although this method takes time but perfect to get accurate results.
In the electrical conductivity method, a TDS meter measures the TDS of water. Here most people have questions in mind what does a TDS meter measure and how to use a TDS meter? The simple and accurate answer is it measures the presence of everything except H2O in water. The concentration of ions present in water is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of the water sample. We measure the TDS through the TDS meter for different purposes. It is done for river, lake, and stream testing, swimming pools, agriculture, hydrophobic cultivations, and other water-related problems.
Check Out: Best Water Softener Systems in the UK
Water Hardness
The hardness of water is basically the presence of high mineral content in water. This high mineral content dissolves in water when water flows through limestone and chalk. These rocks consist of magnesium and calcium carbonates and dissolve in water to make them hard.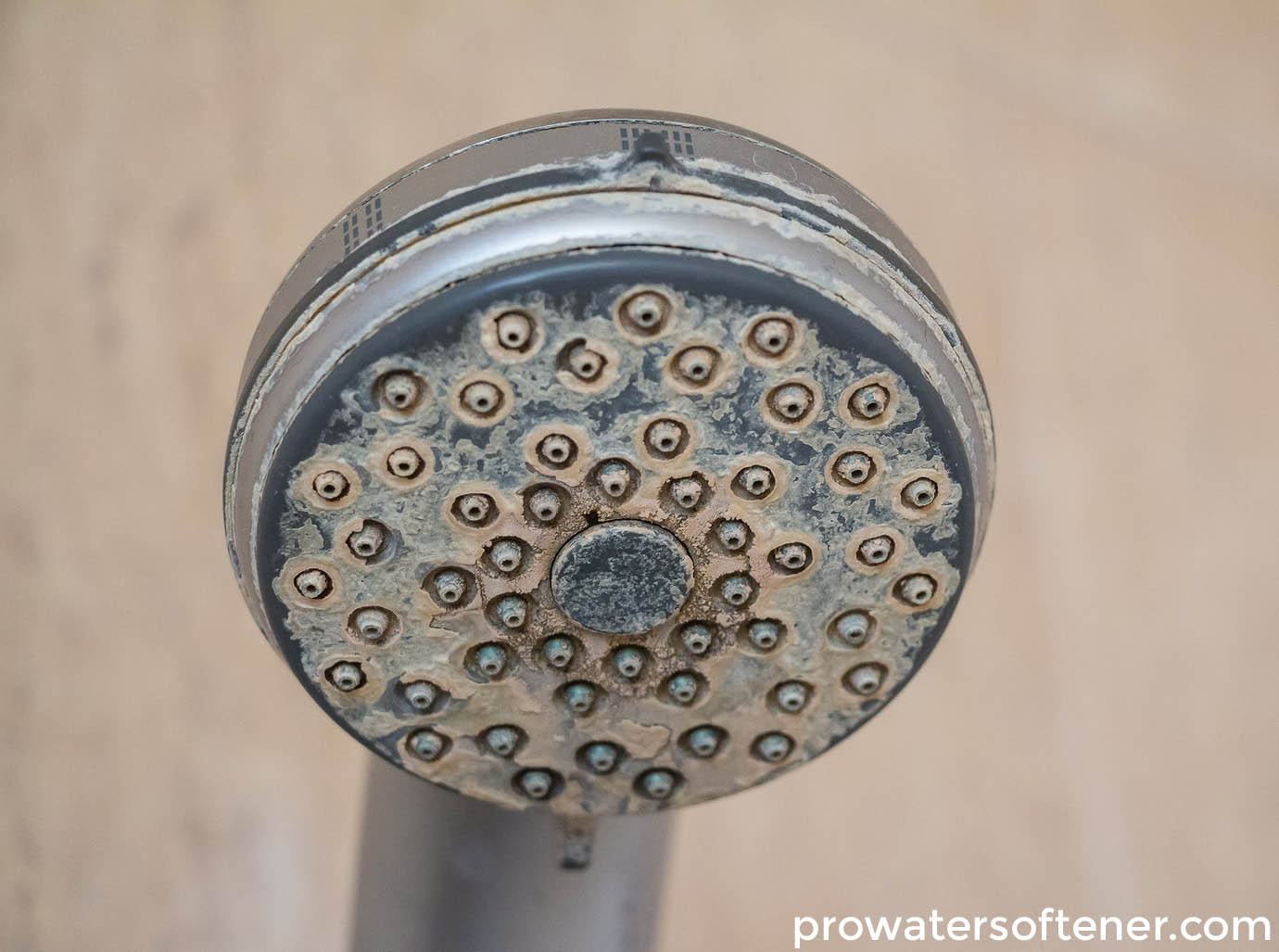
- Temporary Hardness
- Permanent Hardness
Temporary Hardness:
Magnesium and calcium carbonates are dissolvable in water. When these bicarbonate minerals are dissolved or present in water, they make the water temporarily hard. These minerals form carbonate and bicarbonate anions along with calcium and magnesium cations when mixed in water. Water hardness through these bicarbonate minerals is temporary and can be removed by boiling water or adding lime to hard water.
Permanent Hardness:
The permanent hardness of water occurs when sulfates and chlorides of calcium and magnesium dissolve in water. When the water is heated, these minerals are not hasty. That’s why permanent hardness cannot be removed by adding lime or boiling water. To remove permanent hardness, you need to use a water-softening system.
Measuring Water Hardness:
Measuring the water’s hardness is very easy. It is measured in mol/L or mmol/L units. The simple method of testing water hardness testing is through a soap test kit. You required a little bottle or testing kit with a line marked on it. Add water to the line and then add a drop of soap. After this shake the bottle and look for suds. If suds appear, it means water is good, and if not that means it is hard water. Adding more drops of soap will lead to more degrees of hardness.
Check Out: 15 Water Softener Shower Heads for the bathroom
TDS vs Hardness
| Hardness | TDS |
|---|---|
| Hardness is defined as the presence of high mineral content dissolved in water. | TDS abbreviates for Total Dissolved Solids. |
| The hardness of water occurs due to calcium and magnesium carbonates or their chlorides and sulfates. | TDS occurs due to organic matters and inorganic salts when they are dissolved in water. |
| It is measured either through laboratory test to simply through water hardness testing kits. | It measured by gravimetric method and electrical conductivity analysis. |
| Unit of measurement is mol/L or mmol/L | Unit of measurement is ppm |
| Hard water causes a white layer on any surface where it is used e.g. white layer on the shower, walls, etc. And it changes the taste of water. | Measurement of TDS are beneficial for river, stream, lake and swimming pool testing, etc. |
How To Test Water Hardness With A TDS Meter
TDS stands for Total Dissolved Solids. It’s the measure of all of the material that is dissolved in your water. A TDS meter actually measures the electrical conductivity of the water, after which it calculates the TDS value. One thing you can’t do with a TDS meter is to use it to figure out how well your softener is working. This doesn’t work because of the nature of how water softening works. A water softener is an ion-exchange device – it grabs onto calcium and magnesium ions (aka hardness) and exchanges them for sodium. Well, sodium carries the same electrical charge as hardness. So the TDS reading of hard water and soft water is pretty much identical even if the water has softened perfectly.
Check Out: Top Portable Water Softener for RV in 2024
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can water softeners reduce TDS?
We use water softeners to reduce the number of hard minerals in your home’s water. However, water softeners do not reduce total dissolved solids (TDS). TDS is the measure of all matter which dissolves in the water – inorganic and organic. When water flows through the softening unit, it will pass through a resin and chemical matrix (called Zeolite) that will exchange the calcium and magnesium ions with sodium ions (salt).
2. Are TDS and hardness the same?
TDS and hardness are water quality parameters. The main difference between TDS and hardness is that TDS include inorganic and organic substances that cannot be filtered through a filter paper. However, hardness is due to the presence of magnesium and calcium salts of carbonate, sulfate, and chloride.
3. Can hardness be higher than TDS?
When there is hard water, the specific quantity of the TDS is made up of hardness minerals, but a lot of it won’t be. So, your TDS value will always be significantly higher than the hardness value. The other thing you can’t do with a TDS meter is to use it to figure out how well your softener is working. This doesn’t work because of the nature of how water softening works.
4. Is low TDS water is harmful?
Low TDS water is defined as that containing between one and 100 milligrams per liter (mg/L) of total dissolved solids (TDS). This is typical of the water quality obtained from distillation, reverse osmosis, and deionization point-of-use water treatment available to consumers in the world. However, scientific data clearly demonstrate that the consumption of low TDS water will not lead to harmful effects on the human body.
5. What affects water hardness?
Hardness is caused by compounds of calcium and magnesium, and by a variety of other metals. General guidelines for classification of waters are 0 to 60 mg/L (milligrams per liter) as calcium carbonate is classified as soft; 61 to 120 mg/L as moderately hard; 121 to 180 mg/L as hard; and more than 180 mg/L as very hard.
Check Out: Best Water Test Kits for Home Water in 2024
Conclusion
Concluding that whether it is TDS or hard water, both are harmful to your health. TDS consists of inorganic salts and dissolved organic elements that cannot filter through a filter paper. Whereas hardness is due to the dissolving of calcium and magnesium carbonates. Both of them make the water totally another type of water that is harmful. Always keep analyzing whether your water taste or color is changing or not to make sure use pure water for better health.

Steve Smith is a United State Licensed Plumber with over 18 years of plumbing experience. Steve has conducted residential and commercial plumbing jobs throughout the state and currently works for one of California’s largest plumbing companies. When he’s not working, Steve enjoys spending time with his daughter and son.



![Can you drink water from a water softener? [Important to Know] drinking soft water](https://prowatersoftener.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/drink-water-from-softener-150x150.jpg)





Leave a Reply